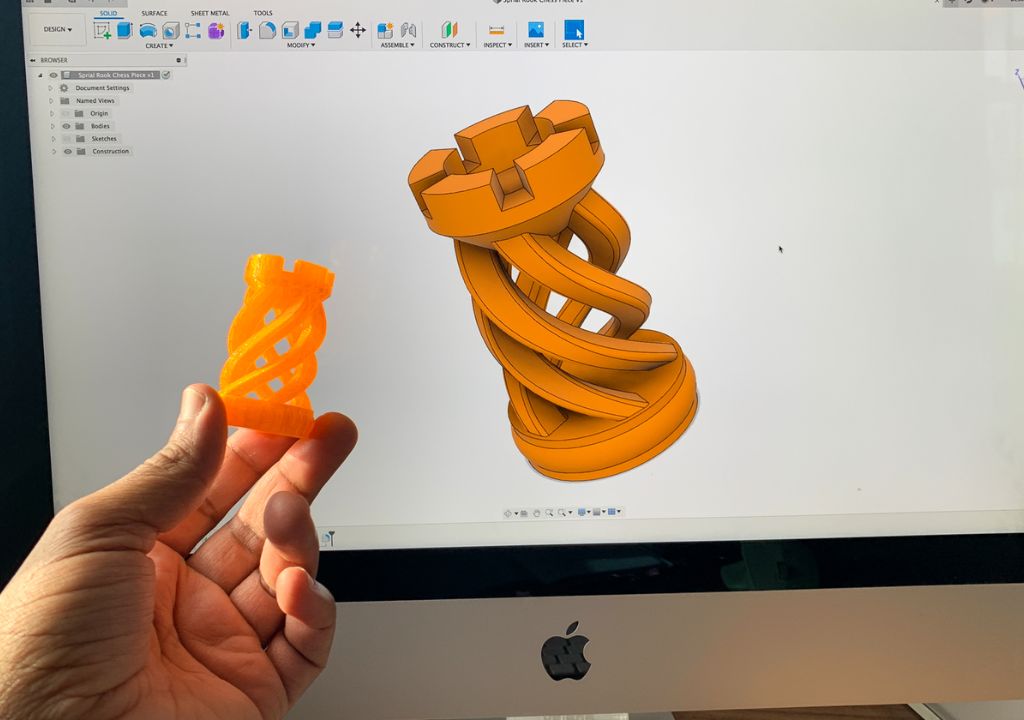
Welcome to the world of Fusion 360 – a comprehensive design and manufacturing platform that empowers creators to bring their ideas to life in three dimensions. In this blog post, we’ll explore the key features and capabilities of Fusion 360, guiding you through the basics and sparking your creativity in the world of 3D design.
Section 1: Getting Started with Fusion 360
1.1 Introduction to Fusion 360:
Fusion 360 is more than just a 3D modeling tool; it’s a complete design and engineering solution. Understand the diverse capabilities, from parametric modeling to simulation and CAM (computer-aided manufacturing).
1.2 Installation and Setup:
Begin your Fusion 360 journey by installing the software and setting up your account. Fusion 360 offers a cloud-based platform, allowing you to access your projects seamlessly from any device.
Section 2: Basic 3D Modeling
2.1 Sketching Basics:
Learn the fundamentals of sketching in Fusion 360. Create 2D sketches that serve as the foundation for your 3D models. Master the use of constraints to control the dimensions and relationships within your sketches.
2.2 Extrude and Revolve:
Explore the extrude and revolve commands to transform your 2D sketches into 3D shapes. Understand how to add depth and complexity to your designs with these foundational modeling techniques.
Section 3: Advanced Modeling Techniques
3.1 Parametric Modeling:
Discover the power of parametric modeling in Fusion 360. Learn how to create intelligent designs by defining parameters that can be easily modified, ensuring flexibility in your projects.
3.2 Assemblies:
Dive into assembling components in Fusion 360. Explore how to create relationships between different parts to simulate real-world interactions. This feature is essential for designing complex systems and mechanisms.
Section 4: Simulations and Analysis
4.1 Stress Testing:
Explore the simulation workspace to analyze how your designs will perform under different stress conditions. Fusion 360 enables you to simulate physical forces and understand potential weak points in your models.
4.2 Thermal and Modal Analysis:
Extend your simulation capabilities by exploring thermal and modal analyses. Understand how your designs respond to heat and vibrations, gaining valuable insights for optimizing your creations.
Section 5: Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM)
5.1 CAM Basics:
Unleash the manufacturing potential of Fusion 360 by delving into the CAM workspace. Learn how to generate toolpaths for CNC machining, turning your digital designs into physical prototypes.
5.2 Post-Processing and Output:
Master the art of post-processing in Fusion 360’s CAM environment. Understand how to generate G-code, the language that instructs CNC machines, and prepare your designs for fabrication.
Conclusion:
Congratulations! You’ve embarked on a journey to master Fusion 360, a versatile tool that seamlessly integrates design and manufacturing. As you continue to explore its features, don’t be afraid to push your creative boundaries and turn your innovative ideas into reality. Happy designing!